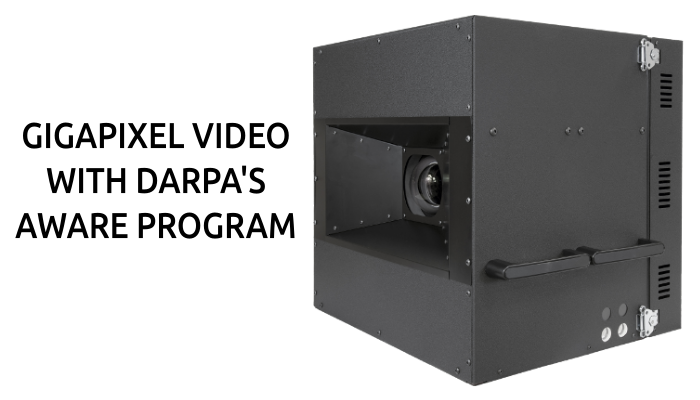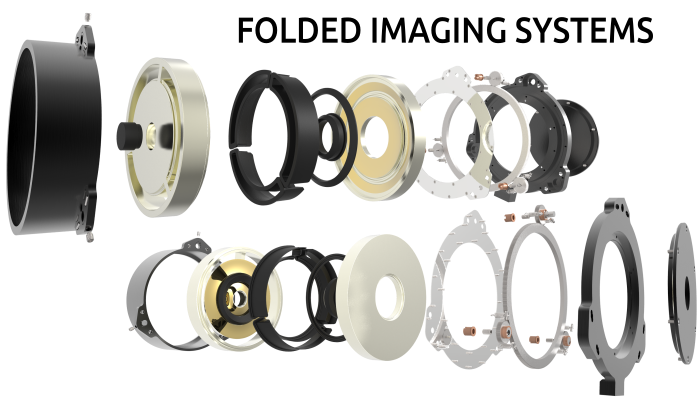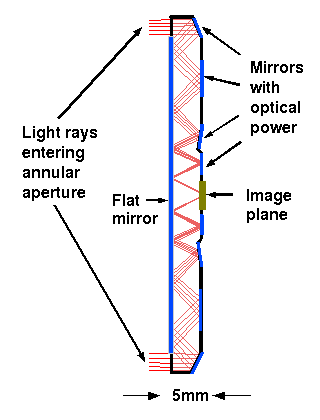
Cross section of folded lens.
Folded Optic
As illustrated in the figure to the right, the MONTAGE demonstrator's architecture differs significantly from a traditional telescopic camera design. An ultra-thin telescopic lens mounts with a conventional 3 mega-pixel CMOS sensor integrated as a vertically aligned disk. The diagram of the innovative UCSD folded optic design above illustrates how the 40mm focal length annular aperture lens is compacted to fit within the 5mm thick volume. The aspheric optical element was fabricated in a diamond machined surface on CaF2. In addition, wavefront corrections were applied to one of the optical surfaces to reduce the longitudinal dependence of the point spread function. Using multi-domain optimization (MDO) techniques developed by CDM-Optics a post-processing step improves the depth of field and increases the tolerance to manufacturing uncertainties. Distant Focus has licensed the folded optic technology from UCSD. Please see our folded optics page for more details.
Electronics and System Integration

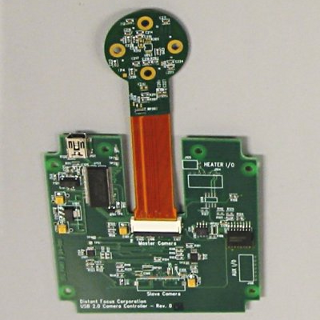
This figure shows the sensor board connected to the USB communications board. The sensor board is actually a rigi-flex PCB; half rigid and half flex.
The demonstrator platform base houses a dedicated USB interface controller that provides interconnectivity to additional computing resources. Distant Focus was responsible for designing the electronic circuit boards; developing firmware and software application interface; designed the packaging; and finally, assembling and testing the combined optical, sensor, and processing system.


The assembled MONTAGE camera. This figure shows an open and closed camera illustrating the finished injection molded enclosure.
Experimental Results
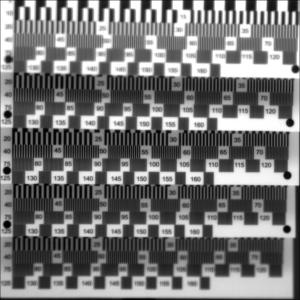
The following images are created from actual camera data from the non-wavefront coded camera, i.e. the traditional folded design. Since the raw data from the camera was in Bayer format, linear interpolation was performed to create these RGB and monochrome images as the case may be.